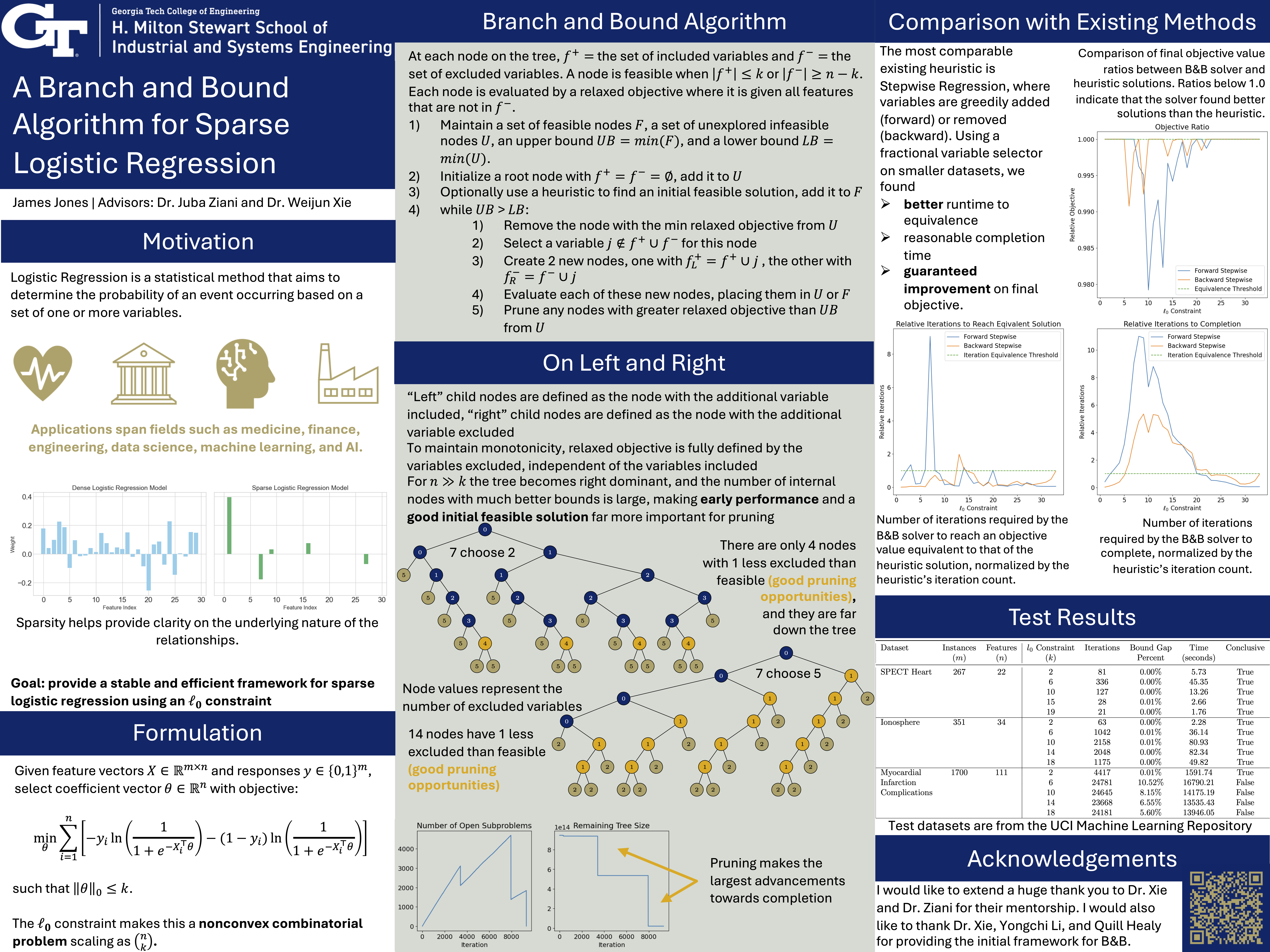
A Branch and Bound Algorithm for Sparse Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression is a statistical method that aims to determine the probability of an event occurring based on a set of one or more variables. This modeling method is used heavily within medical fields, finance, engineering, data science, and AI with supervised machine learning. A key challenge in modern applications is sparsity, identifying a small, relevant subset of features from high-dimensional data. This project introduces a branch and bound framework for sparse logistic regression using the non-convex l0 constraint. The proposed method offers a stable and efficient approach for feature selection, and demonstrates strong performance compared to existing heuristic techniques.
Analyzing Trends and Differences in Discipline Rates in Georgia K-12 Public Schools
Discipline practices in K-12 schools can have a significant impact on students' lives both within and outside of the school environment. This study focused on examining disciplinary trends in Georgia’s K-12 public schools. Utilizing data collected from the Governor's Office of Student Achievement, we analyzed discipline rates over time using time series and compared rates across various demographic groups using mixed-effects binomial regression models. The analysis showed a generally consistent decline in overall discipline rates, with notable deviations during the years affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. There were differences in discipline rates across racial, sex, economic status, disability status, English learner status, and school level subgroups. The odds ratios among the comparisons ranged from 0.27 to 2.74. To further expand this research, future analysis could explore the underlying factors contributing to disparities within subgroups and evaluate the impact of behavioral intervention programs on reducing discipline rates.
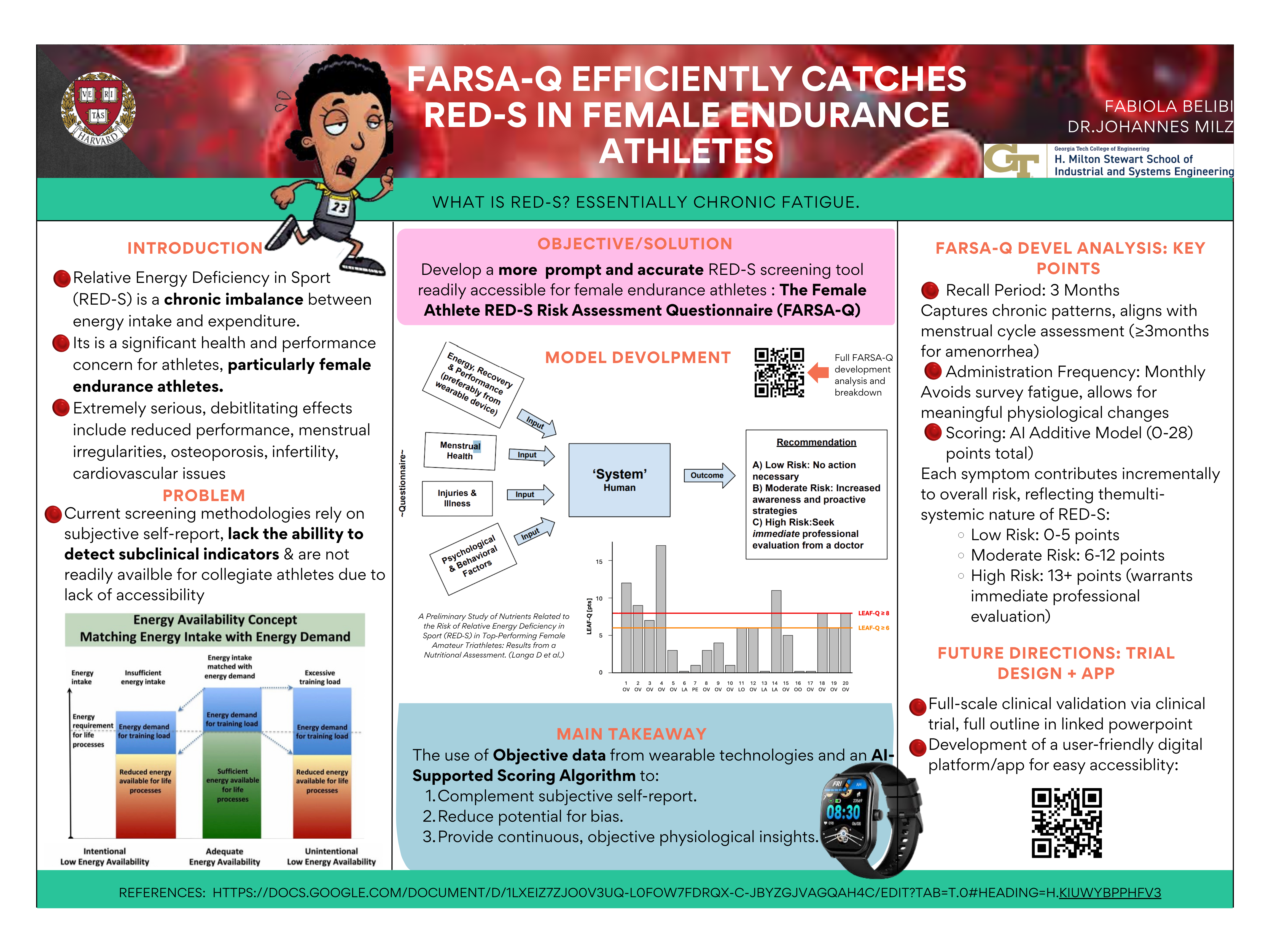
Enhancing Diagnostic Utility of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) in Female Endurance Athletes via AI-supported scoring and Biometric Integration
Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) represents a significant health and performance concern for athletes, particularly female endurance athletes, stemming from a chronic imbalance between energy intake and expenditure. Prompt and accurate identification of RED-S is imperative to prevent severe, long-term physiological consequences and optimize athletic potential. Current screening methodologies, such as the Low Energy Availability in Females Questionnaire (LEAF-Q), while valuable, predominantly rely on subjective self-report, which may lack the sensitivity to detect subclinical indicators and can be susceptible to recall bias. This comprehensive research is aimed at refining a streamlined self-report questionnaire for RED-S risk assessment, enhancing its diagnostic precision through the integration of objective biometric data from wearable technologies, and development of an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-supported scoring algorithm. This innovative approach seeks to provide a more robust, proactive, and personalized screening tool that can eventually be digitalized, thereby providing efficient and effective early detection and management of RED-S in female endurance athletes.
How Well Does the Bi-directed Cut LP Approximate 3-Terminal Steiner Trees?
This project studies the Steiner tree problem, which asks for the minimum-cost network connecting a set of terminal nodes in a graph, possibly using additional non-terminal nodes to reduce cost. To approximate this combinatorial problem, we use the Bi-directed Cut LP relaxation, which allows for fractional edge usage and provides lower bounds on the true solution. A central focus of this work is the integrality gap, which measures the worst-case ratio between the optimal integer solution and its LP relaxation. Understanding and tightening this gap helps evaluate the strength of LP-based methods and their connection to related problems like the 3-cut problem. These questions were investigated through modeling in BARON, an optimization solver capable of computing nonlinear objectives.
LLM Feature Selection for best subset selection
In my research, I expand on LLM feature selection previously used with Lasso machine learning models by combining it with best subset selection instead, using best subset selection algorithms for regression datasets and support vector machines (SVMs) for classification datasets. By combining LLM feature selection with best subset selection, I was able to create a strong and fast framework to produce interpretable and sparse models. LLMBSS has the capacity to expedite the machine learning process and create accurate and explainable models for applications like business, finance, and gene analysis.
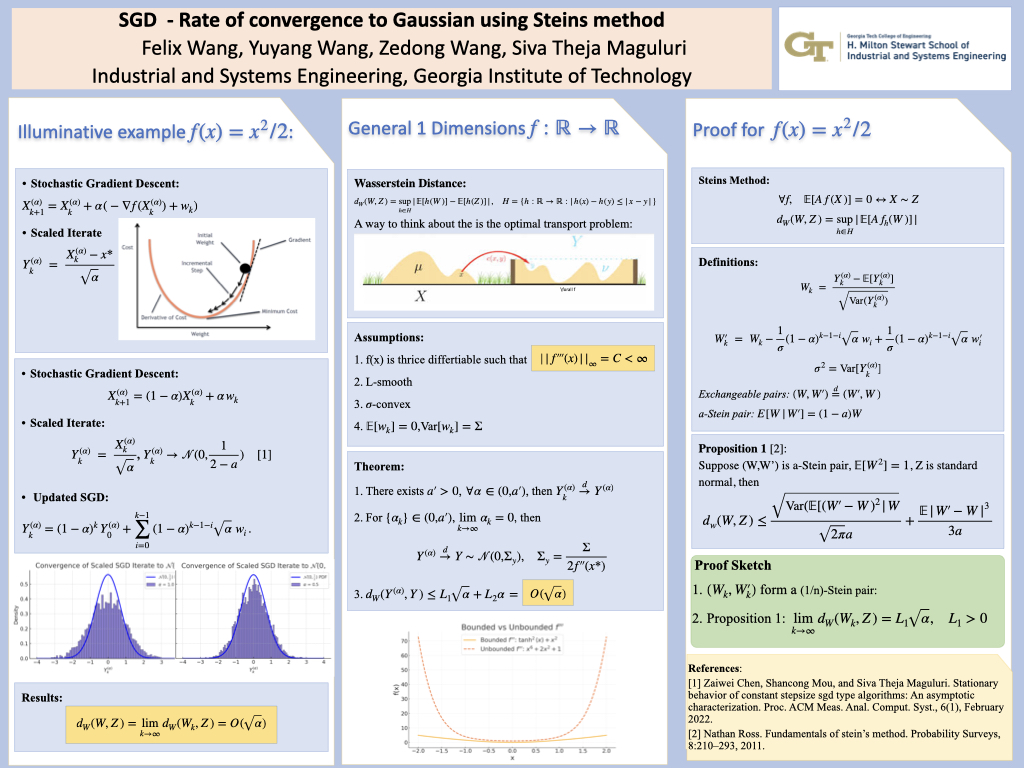
SGD with constant step sizes - rate of convergence to Gaussian using Steins method
Recent work by Zaiwei Chen and Shancong Mou with Professor Siva Theja Maguluri established that stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with constant step sizes converges in distribution to a Gaussian as the step size α→0. However, their analysis does not quantify the rate of convergence between distributions. Our work aims to fill this gap by developing a Stein’s method-based framework to analyze the convergence of SGD in Wasserstein distance. Stein’s method is particularly well-suited for measuring distributional distances to a Gaussian. Using this approach, we derive explicit O(sqrt(α)) bounds on the Wasserstein distance between the stationary distribution of constant-step size SGD and its Gaussian limit, thereby extending the understanding of SGD’s asymptotic behavior.
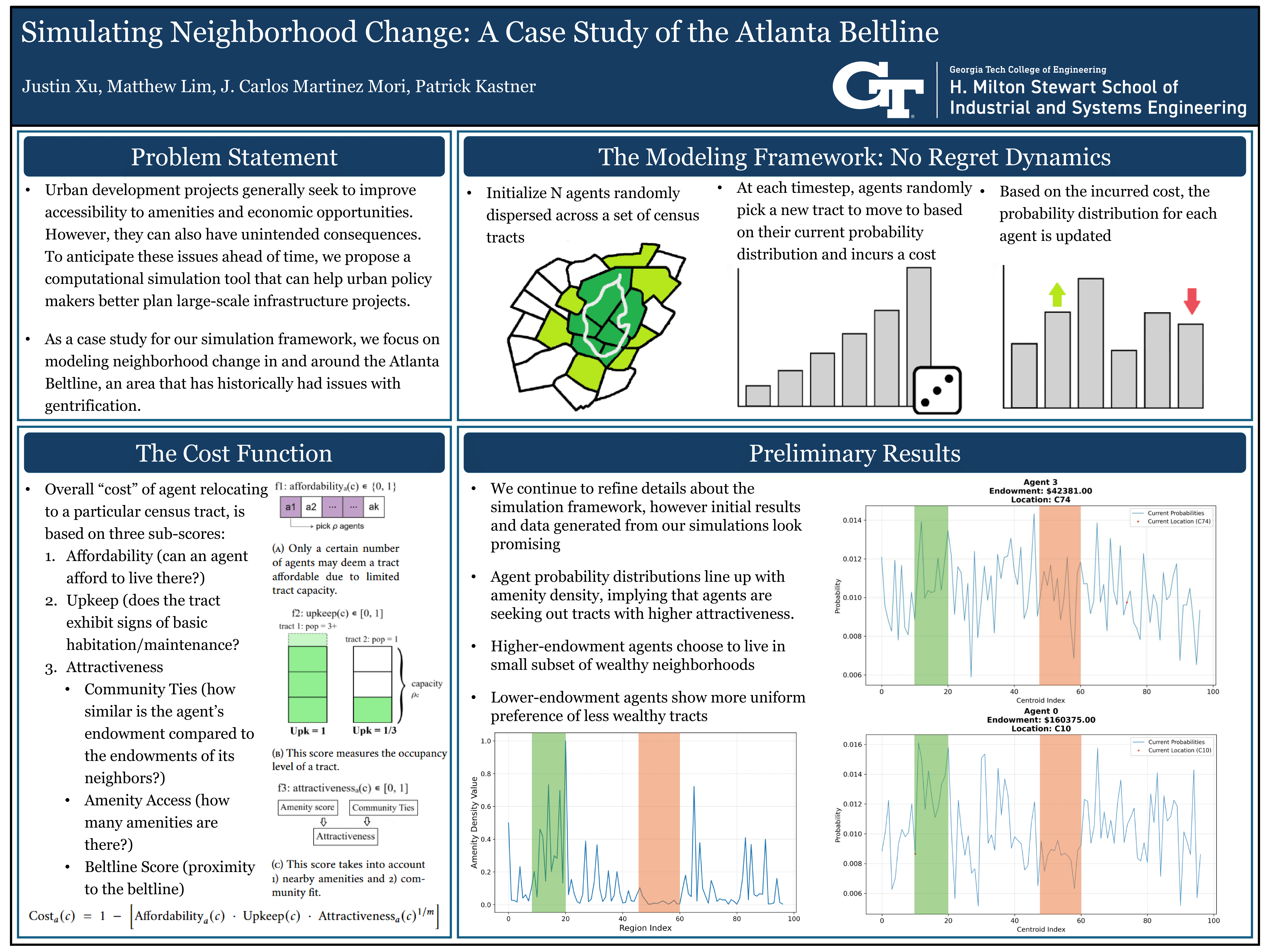
Simulating Neighborhood Change: A Case Study of the Atlanta Beltline
Urban infrastructure projects can have profound and lasting effects on the communities they aim to serve. Although transportation improvements often seek to improve accessibility to amenities and economic opportunities, they can also trigger unintended neighborhood changes, changing demographics, altering affordability, and influencing long-term community composition. Entire neighborhoods may gentrify, displacing long-term residents. In contrast, they may become less desirable, leading to economic stagnation. Traditional urban planning methods struggle to anticipate these because they rely on static models that do not capture the dynamic nature of neighborhood change. To address this challenge, we propose a computational simulation tool that can help urban planners and policymakers better anticipate the long-term consequences of infrastructure projects. Our model is designed to capture key factors such as affordability, attractiveness, and community stability, allowing decision-makers to explore potential outcomes before implementing large-scale changes.
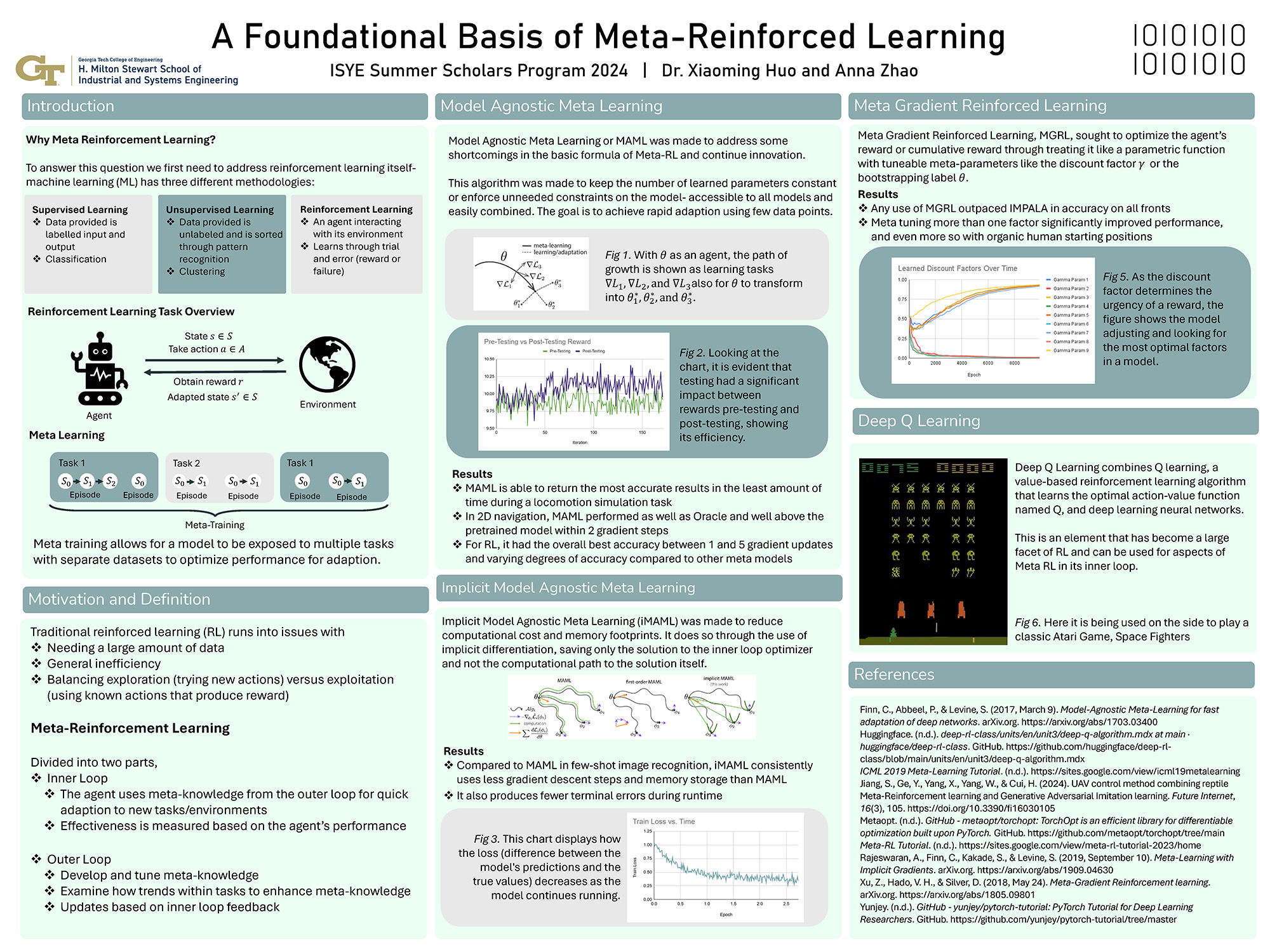
A Foundational Basis of Meta-Reinforced Learning
In this project, we analyze and implement Meta-Reinforcement Learning (Meta-RL) algorithms, including MAML, iMAML, and MGRL, and test them on simple tasks. The project addresses challenges in traditional reinforcement learning, such as the need for large data sets, inefficiency, and balancing exploration with exploitation. Meta-RL mitigates these issues by using meta-knowledge for rapid adaptation. Meta-RL operates through two loops: the inner loop, where meta-knowledge enables quick task adaptation, and the outer loop, which refines this knowledge based on feedback. Our results show that Meta-RL significantly improves over non-Meta-RL by maintaining stable parameters and enhancing cross-model accessibility.
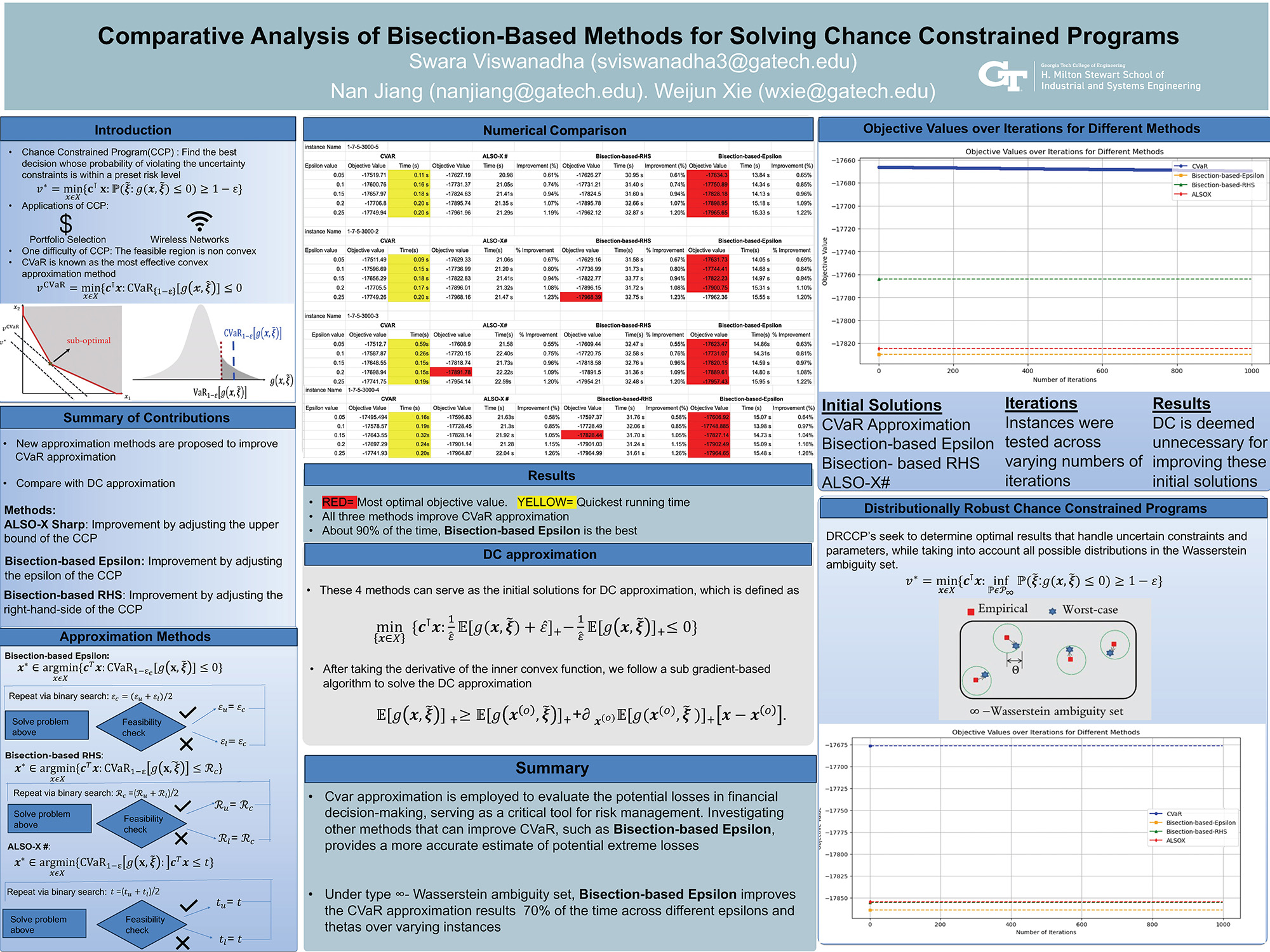
Comparative Analysis of Bisection-Based Methods for Solving Chance Constrained Programs
Chance constrained programming has been widely applied to many applications such as portfolio selection and wireless networks. This project explores the efficacy of three methods for solving chance constrained programs. These methods address the challenge of non-convex feasible regions and provide high-quality and near-optimal solutions. Numerical results show that the proposed “Bisection-based Epsilon” method outperforms the others.
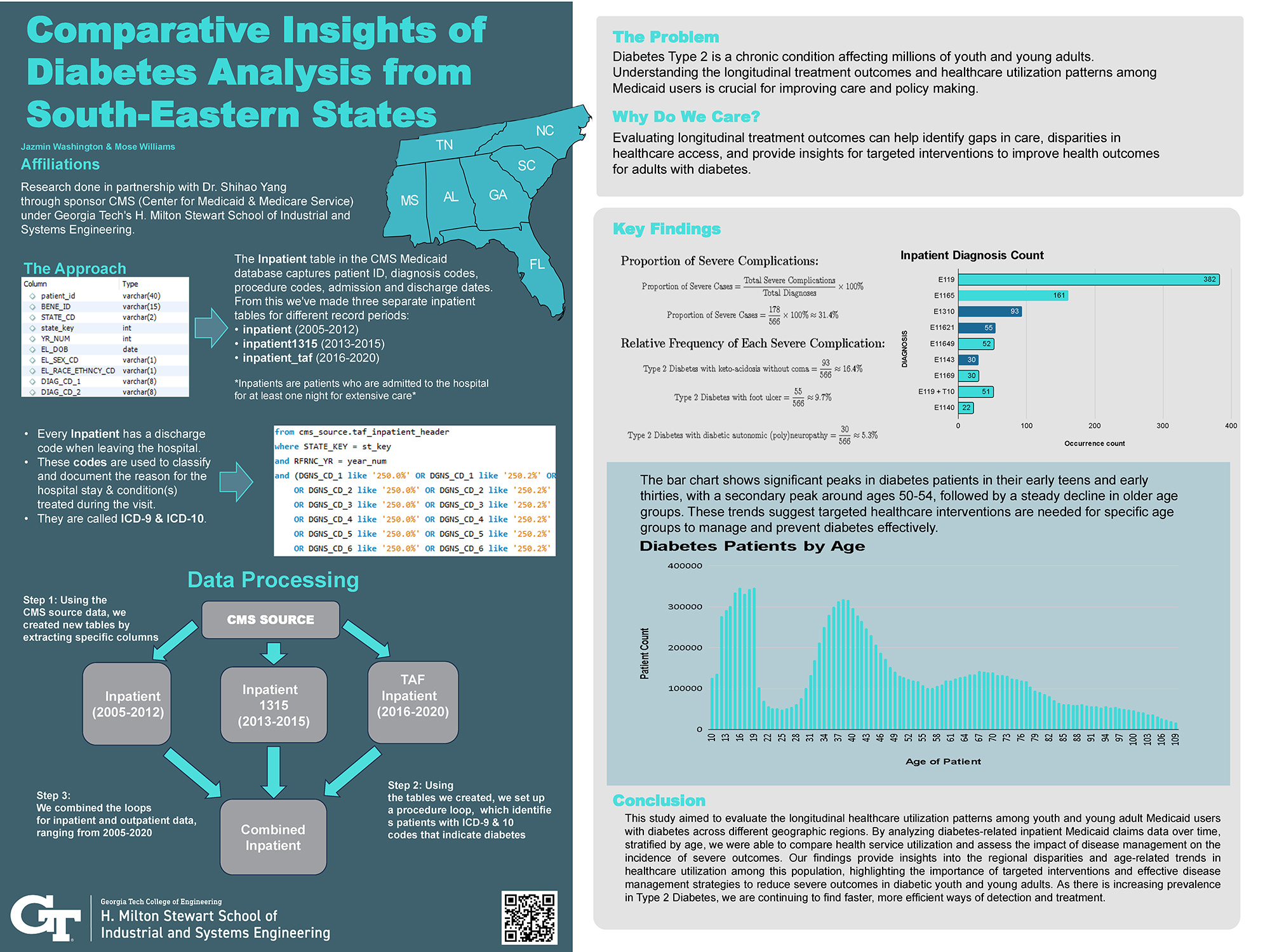
Comparative Insights of Diabetes Analysis from South-Eastern States
This project investigates the longitudinal healthcare utilization patterns among youth and young adult Medicaid/Medicare users diagnosed with diabetes type 2. This study focuses on disparities in health service usage across the Southeastern U.S. region. By analyzing the Diabetes diagnosis and treatment codes of inpatient Medicaid claim data, this study compares health service utilization and assesses the impact of disease management on the incidence of severe outcomes. The findings provide critical insights into regional differences and age-related trends over time in healthcare utilization within this population. This showcases the need for targeted interventions and effective disease management strategies. This study is important given the rising prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes among younger populations, underscoring the urgency of improving detection and treatment methods to reduce severe health outcomes.
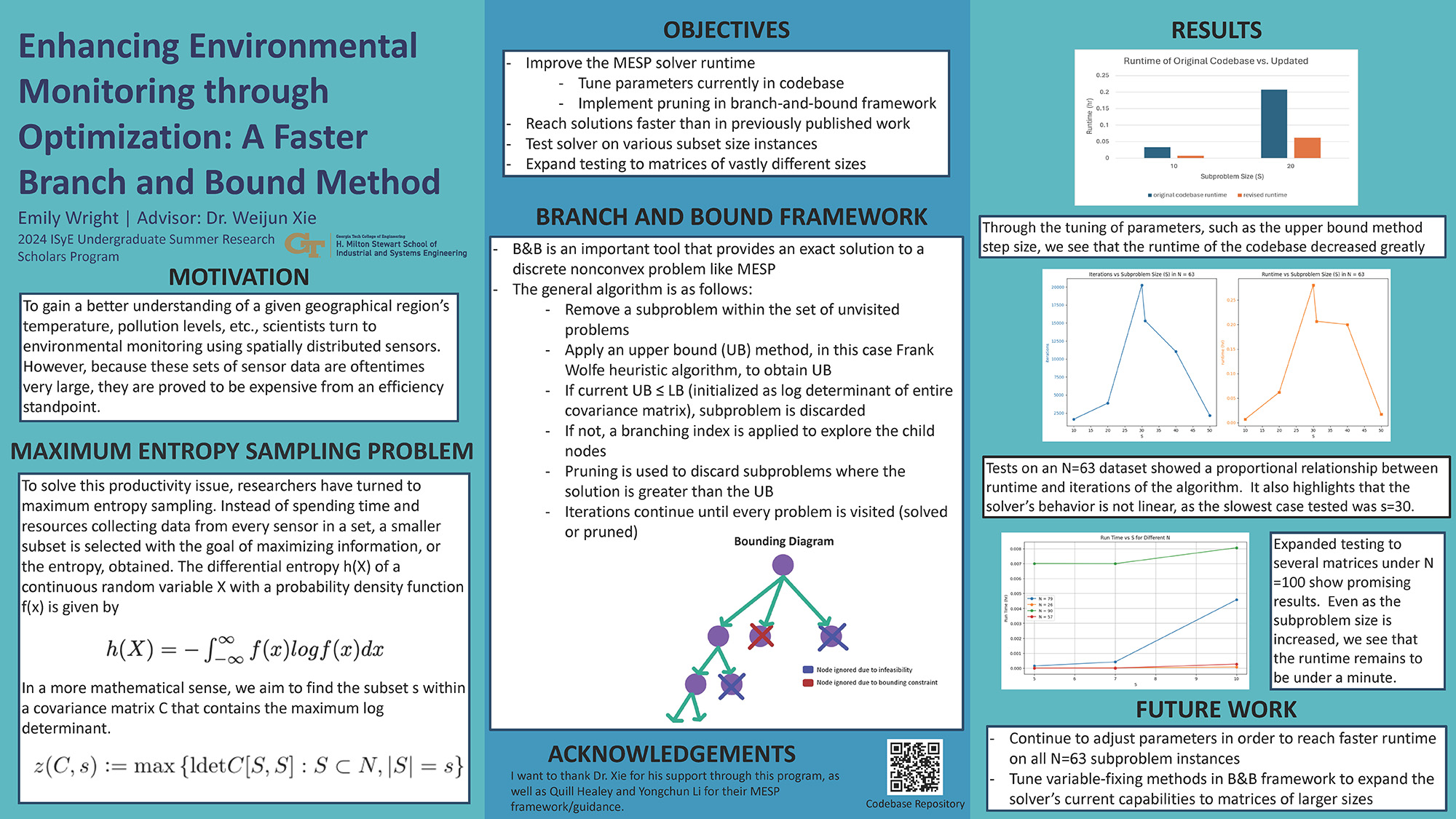
Enhancing Environmental Monitoring through Optimization: A Faster Branch and Bound Algorithm
This project studies the Maximum Entropy Sampling Problem (MESP). MESP optimizes environmental monitoring by using spatially distributed sensors to collect data on variables like temperature and pollution levels. Due to the high cost and inefficiency of using all sensors, the researchers aim to select a smaller subset that maximizes information gain, measured by differential entropy. The project focuses on improving the MESP solver running time by tuning parameters and implementing pruning within a branch-and-bound (B&B) framework. Results indicate that the adjusted parameters can reduce runtime and show promising scalability for larger matrices. The study's methodology and results showcase the effectiveness of the B&B framework in solving discrete nonconvex data analytic problems such as MESP.
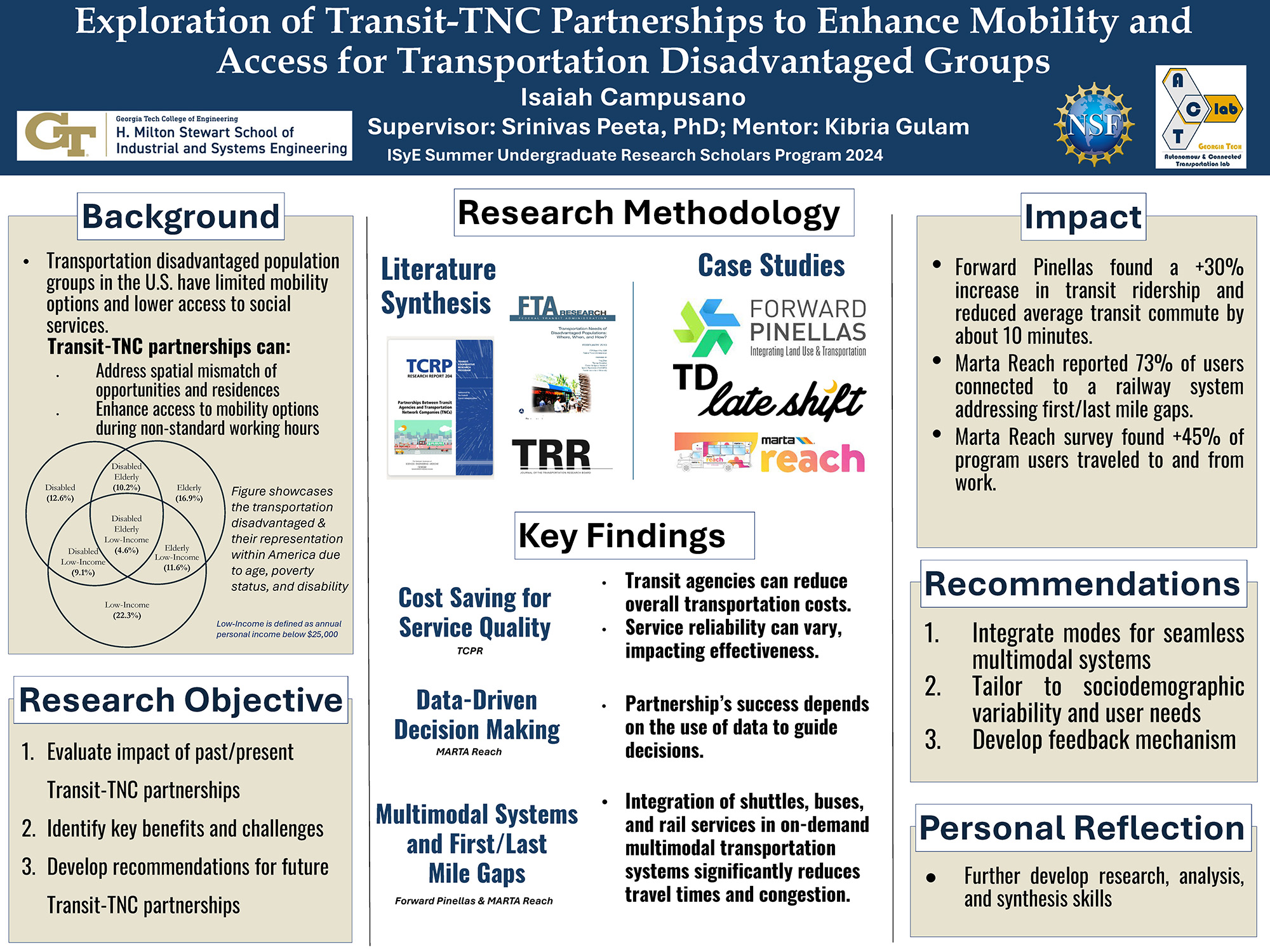
Exploration of Transit-TNC Partnerships to Enhance Mobility and Access for Transportation Disadvantaged Groups
This project examines partnerships between transit agencies and Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) aimed at improving access to essential services for disadvantaged groups, including low-income individuals, seniors, and those with mobility disabilities. By analyzing various past and current partnership programs, such as the MARTA Reach initiative, the study identifies the factors that contributed to the success or failure of these collaborations. Key findings reveal that successful partnerships are characterized by seamless integration, reliable service, and extensive coverage, which can significantly boost transit ridership. However, the study also highlights that many programs failed due to a lack of tailored service models that address the unique needs of different population groups. The synthesis offers valuable insights and recommendations for designing future partnerships that can effectively enhance access to essential services and support the diverse needs of disadvantaged communities.
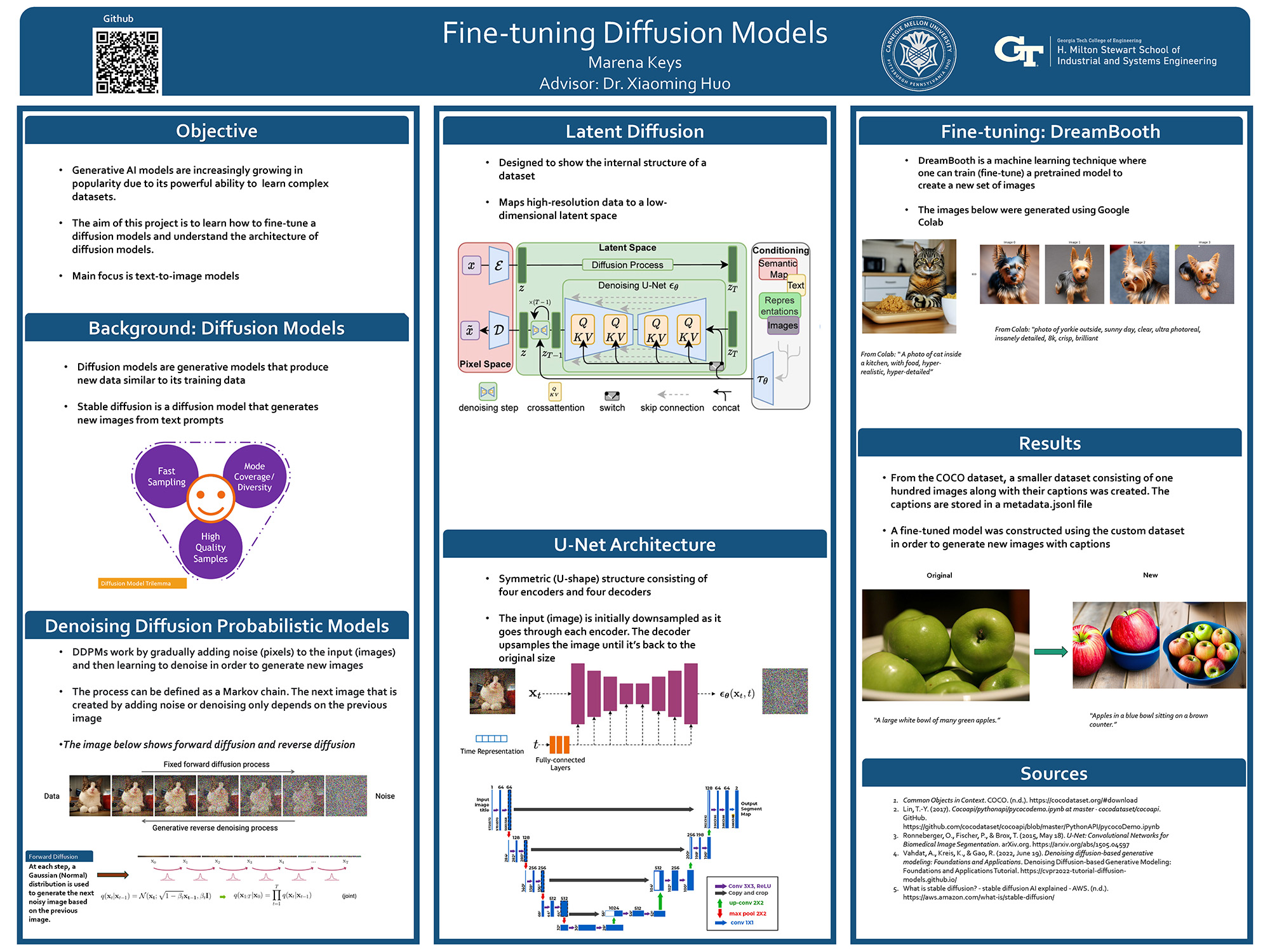
Fine-tuning Diffusion Models
Text-to-image diffusion models have gained significant attention. In this project, we delve into the entire process of the stable diffusion model. Specifically, we first re-implement all network structures of the stable diffusion model, including the denoising model (i.e., U-Net), and verify that it can successfully load pre-trained models from Hugging Face (e.g., Stable Diffusion V1.5). Additionally, we build a complete fine-tuning pipeline, which includes: 1. automatically cleaning up raw data to the required format, 2. fine-tuning the stable diffusion model using the Dreambooth technique, and 3. fine-tuning the model using LoRA with limited computing resources. Finally, we test our pipeline on other datasets (e.g., the Pokemon dataset), and the results show that our pipeline successfully fulfills the fine-tuning task.
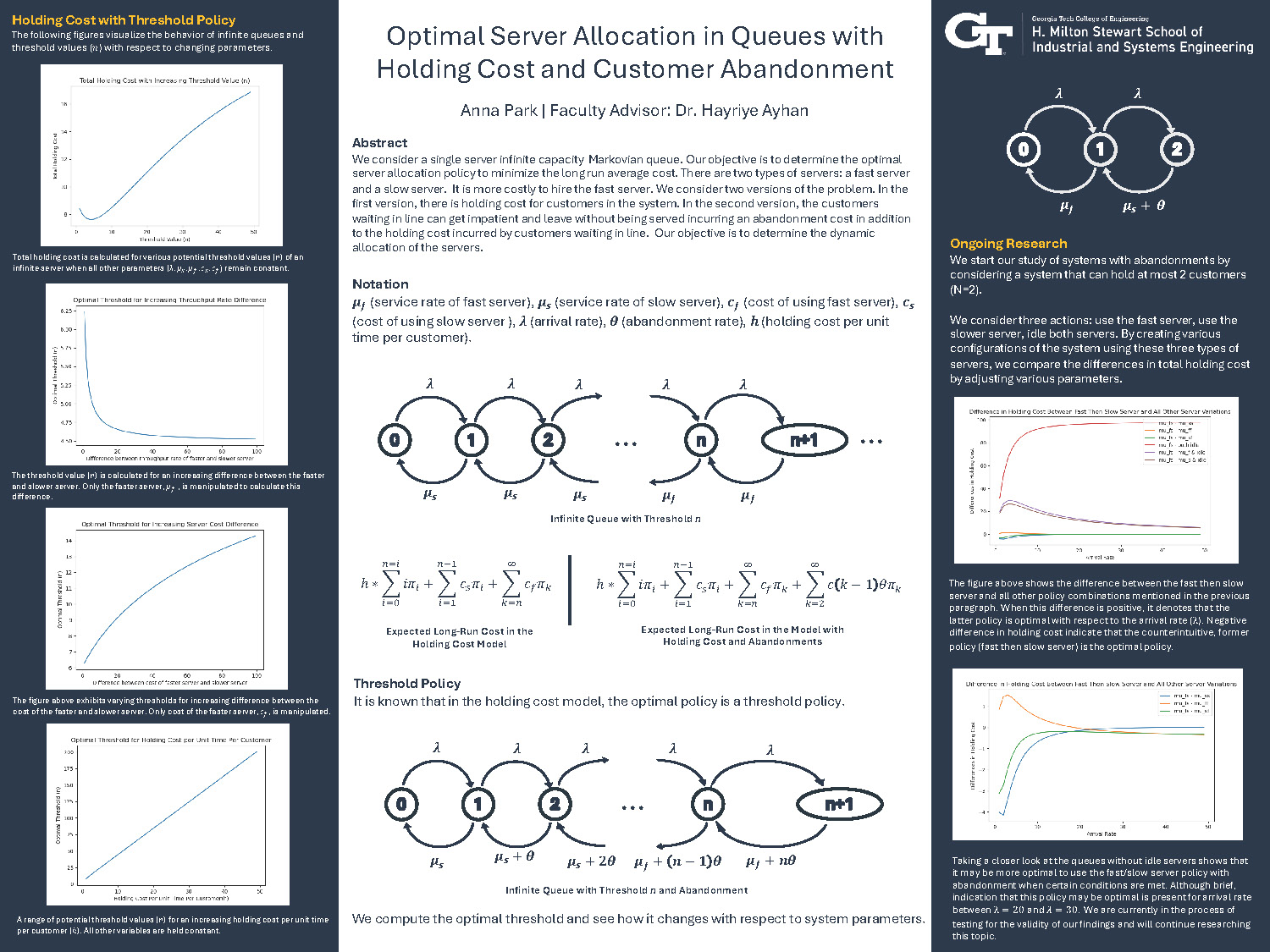
Optimal Server Allocation in Queues with Holding Cost and Customer Abandonment
We consider a single server infinite capacity Markovian queue. Our objective is to determine the optimal server allocation policy to minimize the long run average cost. There are two types of servers: a fast server and a slow server. It is more costly to hire the fast server. We consider two versions of the problem. In the first version, there is holding cost for customers in the system. In the second version, the customers waiting in line can get impatient and leave without being served incurring an abandonment cost in addition to the holding cost incurred by customers waiting in line. Our objective is to determine the dynamic allocation of the servers.
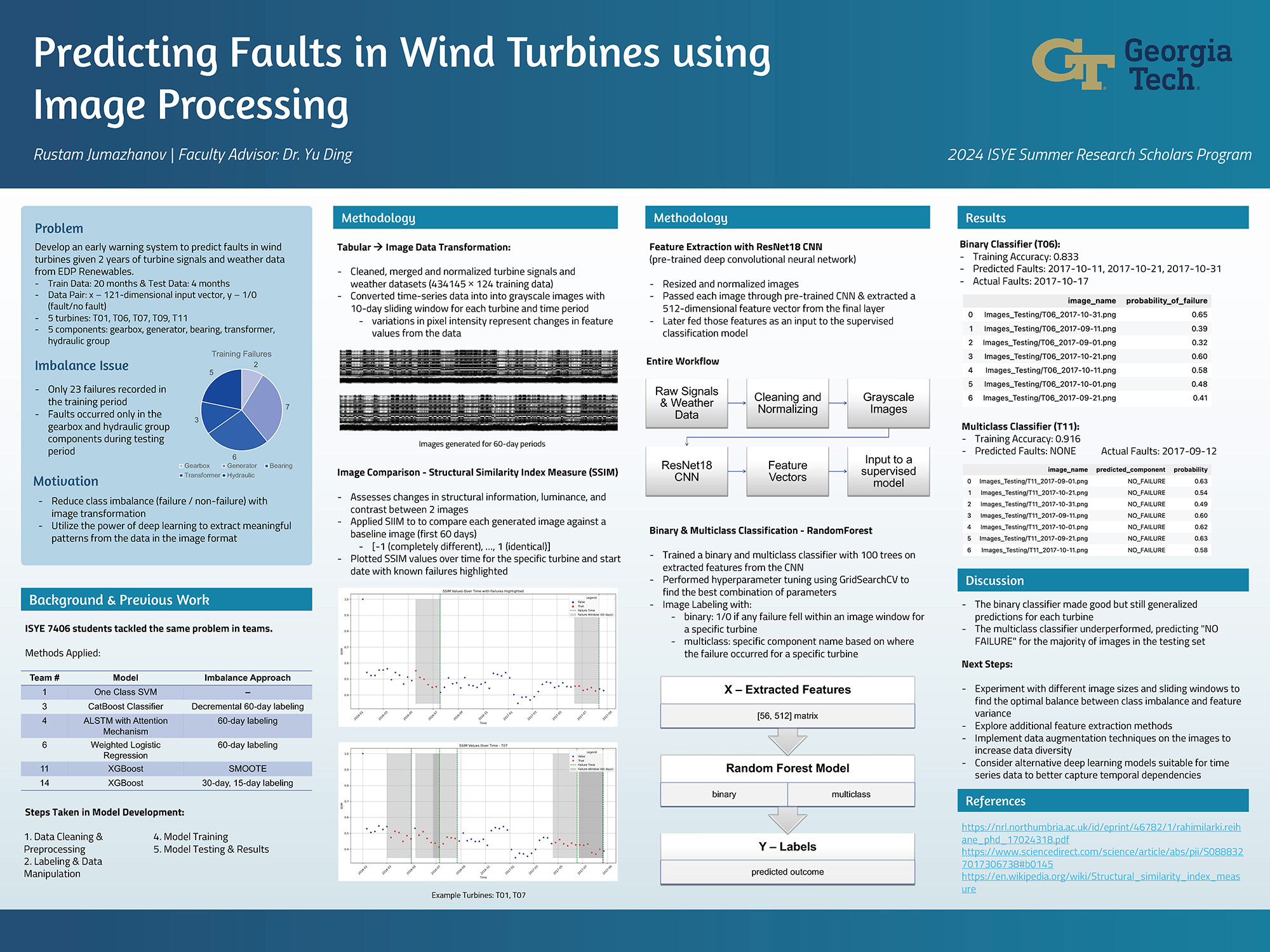
Predicting Faults in Wind Turbines using Image Processing
Wind energy is one of the fastest growing renewable energy sources and now supplies more than 10% of the electricity consumed in the US annually. Under non-steady loads and a harsh operation environment, wind turbines are prone to failures but expensive to repair. High on wind farm operators' wish list is the ability to have an early warning, foretelling the upcoming of major turbine faults, so that the operators can plan for part ordering and crew preparation. This summer project looks into various machine learning-enabled early warning methods and studies their pros and cons. Of particular interest is the question of whether it would be advantageous to convert the wind turbine operational data into images and then use the state-of-the-art deep learning-based image anomaly detection tools to identify the anomalous conditions leading to a turbine failure.
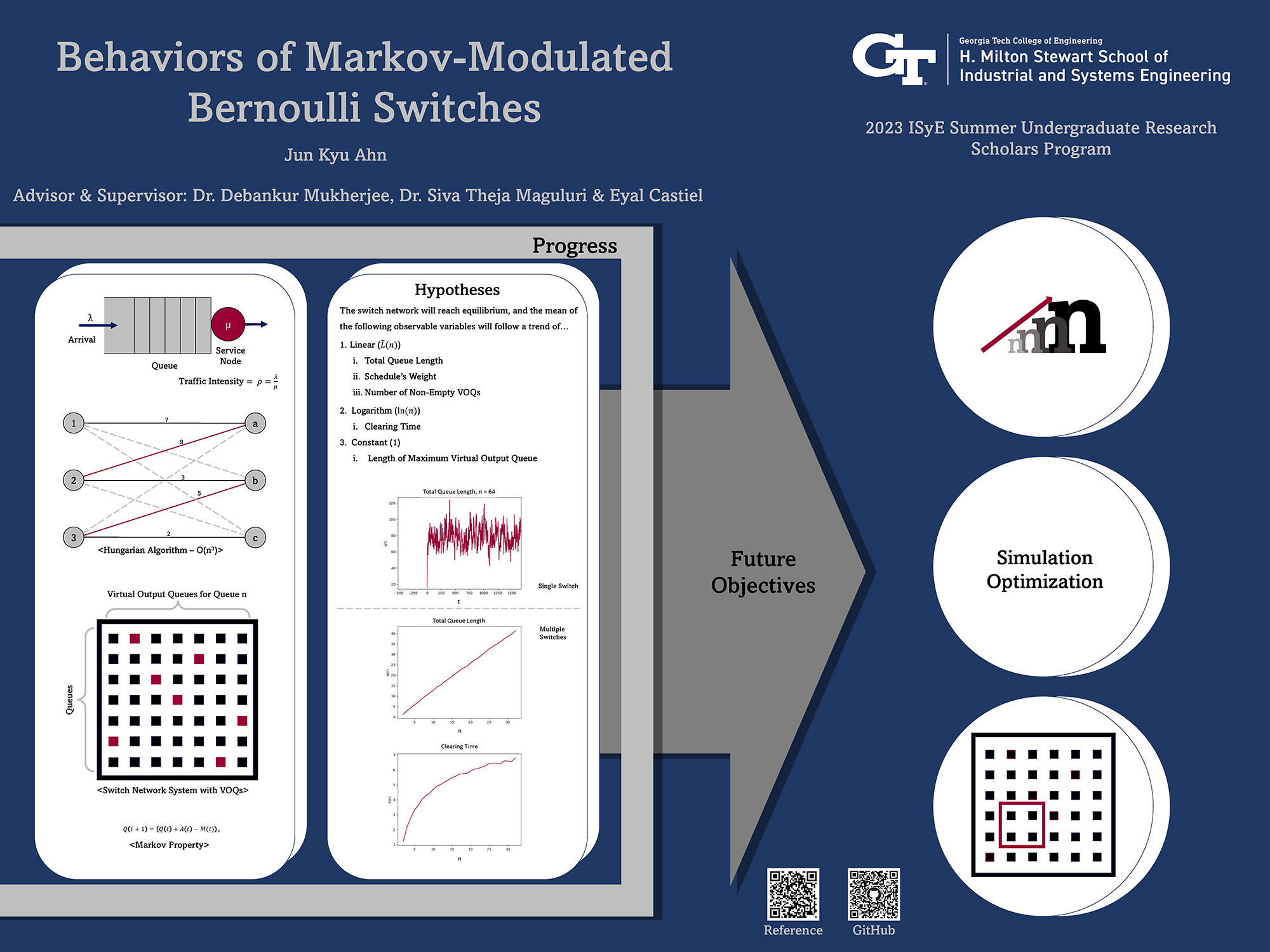
Behaviors of Markov-Modulated Bernoulli Switches
The expansion of cloud computing industries has spurred efforts to understand the behaviors of large switch networks due to the increasing scale of data we use and store. This study focuses on observable phenomena such as the total queue length and clearing times from switch networks to observe their stationary behavior in respect to 'n', the size of the switch network. The stability of switch network is assured by the max-weight algorithm that serves jobs in high-performance polynomial runtime complexity. While job scheduling relies on the current state of the queue lengths within the switch network, the state of queue lengths within the switch follows a discrete time Markov chain. In this research, we implemented a simulation of switch network using the Hungarian algorithm in Python, and this study aims to identify the stationary distributions of switch network phenomena with respect to 'n'.
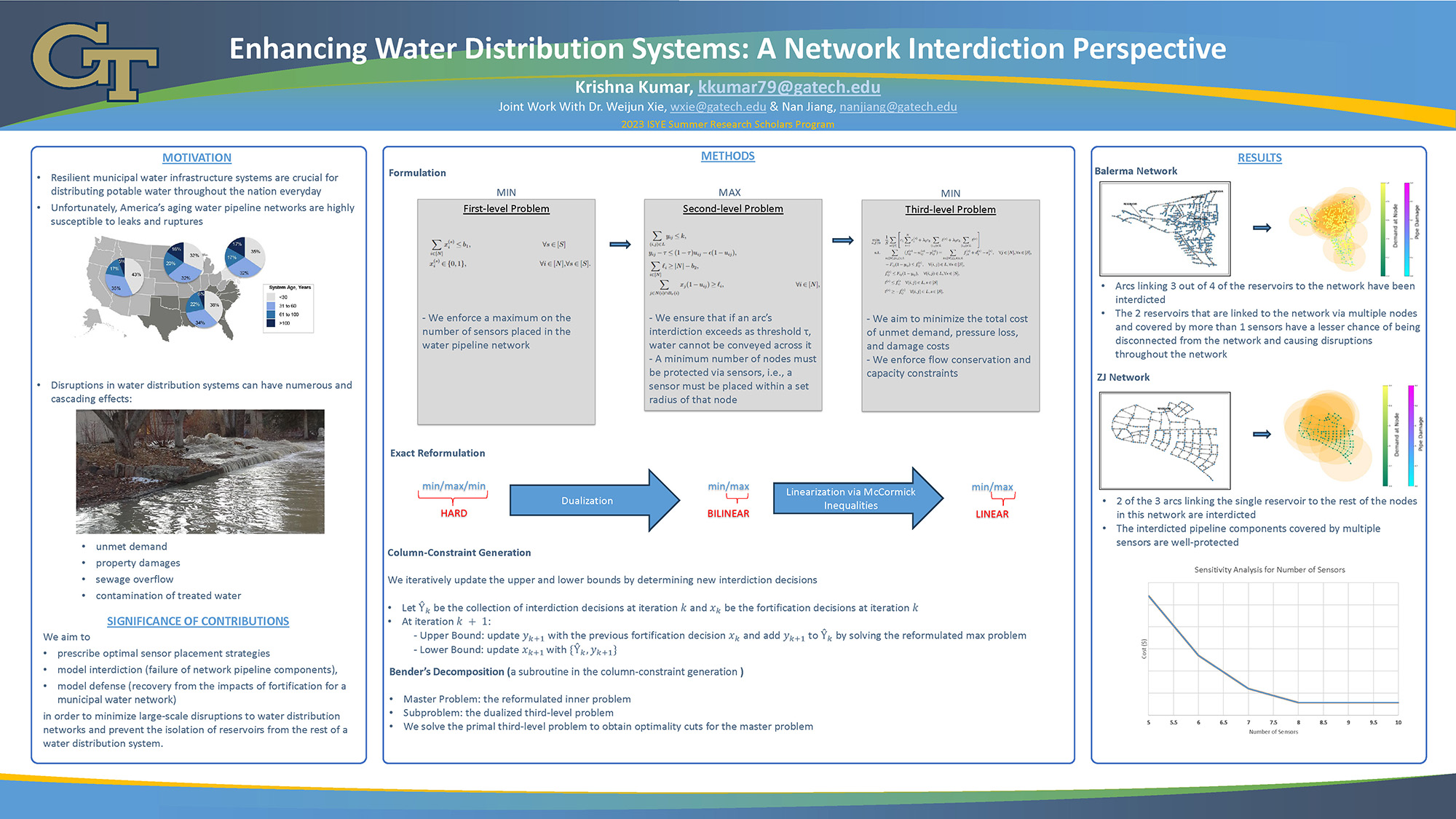
Enhancing Water Distribution Systems: A Network Interdiction Perspective
Pipe failure is a common occurrence in America's water distribution networks. In this paper, we propose a tri-level stochastic network interdiction formulation to model the fortification (via sensor placement), attack (i.e., failure of pipeline components), and defense (i.e., recovery from the impacts of interdiction) for a water pipeline network. We adapt column-constraint generation for our algorithmic approach to solve for the optimal solution. In the final section of our paper, we apply our model and approach to a few well-studied networks and discuss our numerical studies.
Exploring Nutrient Intake Habits: A Survey on Food Consumed In the Past 24 Hours
Nutrition have played a fundamental role in shaping our health and well-being. The foods we consume daily provide the essential nutrients our bodies need to function. Therefore, understanding nutrient intake is crucial because it helps us make informed, positive dietary choices. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) has been pivotal in collecting health data of U.S. residents, including daily dietary intake, since the 1960s. Commencing in 2000, they have consistently published their annual data. However, due to the pandemic, they stopped the program. As of now, the most recent dataset, spanning from 2017 to 2020, was published in 2022. Thus, my research contributes to the ongoing exploration of nutrient intake trends.
Maximin Fair Allocation
Fair distribution in allocation problems is a well-studied problem where a variety of fairness criteria have been studied. In this project, we study the maximin fairness criteria that generalizes the classical cake cutting problem to the setting for indivisible goods. For two players, “you divide and I choose” strategy satisfies the fairness criteria but such a simple strategy does not exists for three players. The project aim to understand how good maximin shares exist for three and more players. The project also explores the connections to other fairness criteria including envy-freeness and average share.
Navigating Nutritional Neccessities: Exploration of Food Deserts in U.S. College Environments
This project delves into the impact of highly processed food on health, spotlighting the United States' notably low Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE) compared to other developed nations, as highlighted by WHO data from 2000 to 2018 (before Covid pandemic). HALE measures years living without assistance. The overconsumption of highly processed food is one of the major contributors to poor health performance. This research employs online resources, government survey results, and field studies to examine dietary habits, connecting overconsumption of processed foods to the U.S.'s shortened HALE and exploring broader health implications.
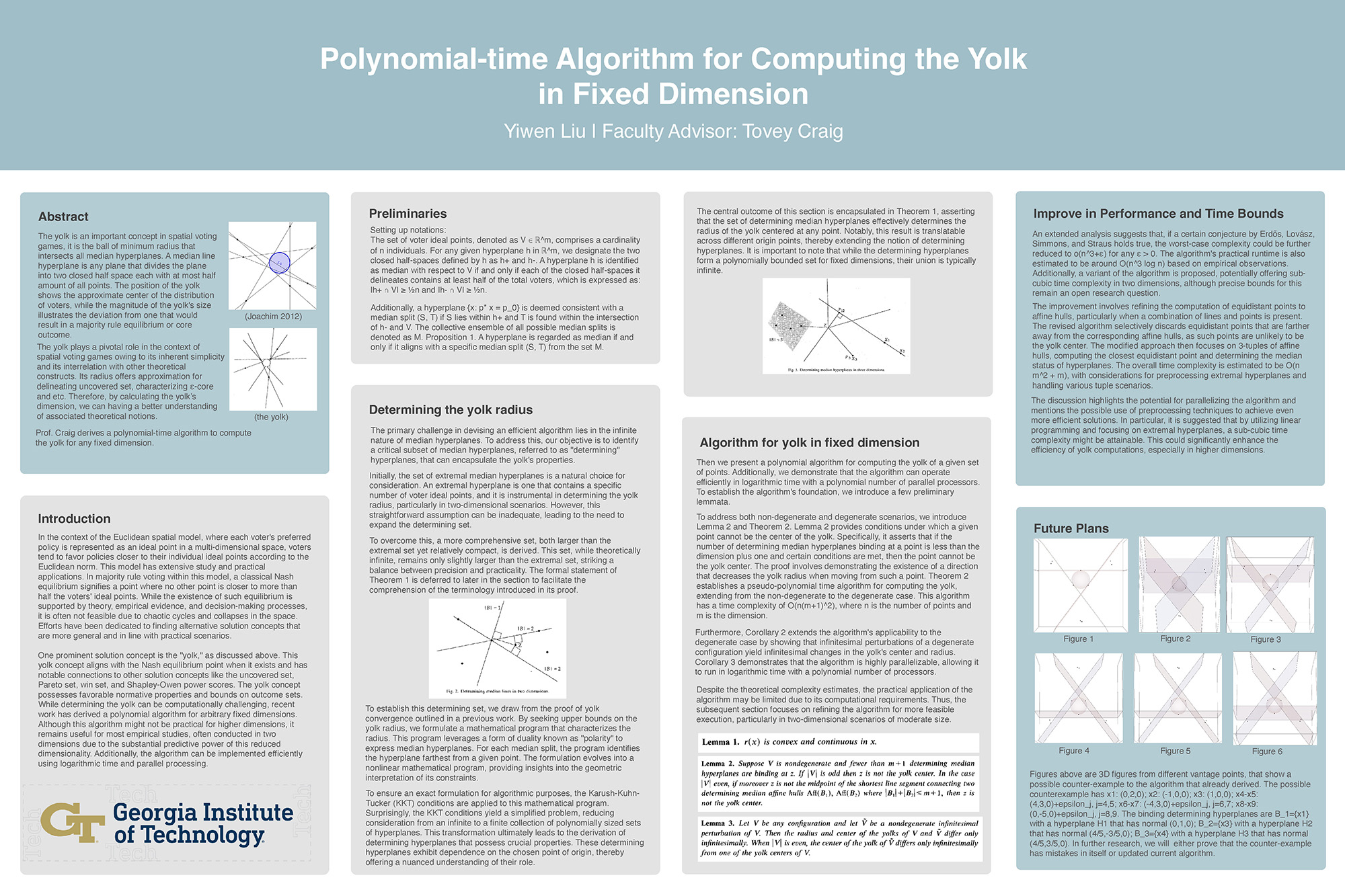
Polynomial-time Algorithm for Computing the Yolk in Fixed Dimension
In spatial voting games, the concept of the yolk is crucial as it represents the smallest sphere intersecting all median hyperplanes and reflects the central tendency of voters' preferences. Median hyperplanes are those that split the voter ideal points into two groups, with no more than half on either side. The yolk's radius is not just a measure of central tendency but also informs on the stability of majority rule outcomes, often disrupted by strategic voting and coalitional dynamics. The research poster also presents 3D visualizations from various perspectives, illustrating a potential counterexample to an existing algorithm. This counterexample is defined by specific coordinates and binding hyperplanes with distinct normals. The ongoing research aims to ascertain whether this counterexample reveals an inherent flaw or if it necessitates a refinement of the current algorithm, thereby enhancing the precision of yolk calculation in spatial voting scenarios.
Surprise? Parents might like changing Survey Context school schedules
Following a move by California to mandate later start times for high school students, the San Francisco Unified School District (SFUSD) proposed new optimized start times for the 2022-2023 school year. School start times are a complex issue that affect families, teachers, and staff in many different ways. After the change, we conducted a survey of families and staff from SFUSD to assess their thoughts on the change. We found that families tend to prefer moving later rather than moving earlier, and that stakeholder satisfaction may depend not only on the outcome of the process but also on its perceived fairness.